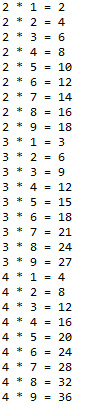[TIL] 이노베이션캠프 in 동북 Part 03. 조건문과 반복문
Part 03. 조건문과 반복문
IF
IF - else IF - else if - else
중첩 if
블록 {}
SWITCH
FOR
중첩FOR
향상된 FOR
임의의 정수 만들기
WHILE
do-while
break와 continue
이름붙은 반복문
Part 03. 조건문과 반복문
Flow Chart : 순서도 및 흐름도
어떠한 일을 처리하는 과정을 순서대로 간단한 기호와 도형으로 도식화 한 것을 의미함.
알고리즘이나 프로그램의 논리 혹은 그림으로 표현하는 방법
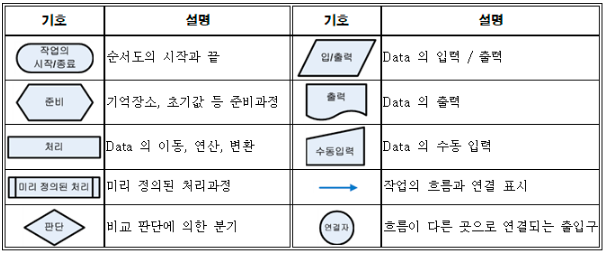
- 위 기호들을 사용하여 프로그램의 순서를 표현할 수 있다.
Flow Chart 예시 1

Flow Chart 예시 2

FlowChart 예시 3

참고 : https://app.diagrams.net/ (Flow Chart 쉽게 그릴 수 있는 사이트)
IF
if(조건식 { 조건식의 결과가 참일 때 실행하고자 하는 문장;
}
예시 코드
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class Control1_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char ch = 'b';
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
System.out.println("해당 문자는 영문 소문자입니다.");
}
}
}
|
cs |

If - else
if(조건식) {
조건식의 결과가 참일 때 실행하고자 하는 문장;
} else {
조건식의 결과가 거짓일 때 실행하고자 하는 문장;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class Control1_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char ch = 'Z';
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
System.out.println("해당 문자는 영문 소문자입니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("해당 문자는 영문 소문자가 아닙니다.");
}
}
}
|
cs |

if - else if - else
if (조건식 1) {
조건식 1의 결과가 참일 때 실행하고자 하는 문장;
} else if ( 조건식2) {
조건식2의 결과가 참일 때 실행하고자 하는 문장;
} else {
조건식 1의 결과도 거짓이고, 조건식 2의 결과도 거짓일 때 실행하고자하는 문장;
즉. 위의 어느 조건식에도 만족하지 않을 때 실행
}
- 여러 개의 조건식을 포함한 조건식임.
- else if 가 여러번 사용될 수 있음
- 마지막 else 블럭을 생략이 가능
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
class Control1_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char ch = 'p';
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
System.out.println("해당 문자는 영문 소문자입니다.");
} else if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') {
System.out.println("해당 문자는 영문 대문자입니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("해당 문자는 영문자가 아닙니다.");
}
int score = 70;
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A등급입니다.");
} else if(score >= 80) {
System.out.println("B등급입니다.");
} else if(score >= 70) {
System.out.println("C등급입니다.");
}
}
}
|
cs |

중첩 if
if(조건식1) {
조건식1의 결과가 참일 때 실행하고자 하는 문장;
if(조건식2) {
조건식1과 조건식 2의 결과가 모두 참일 때 실행하고자 하는 문장;
} else {
조건식1의 결과가 참이고, 조건식2의 결과가 거짓일 때 실행하고자 하는 문장;
}
} else {
조건식1의 결과가 거짓일 때 실행하고자 하는 문장;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
class Control1_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 87;
if (score >= 90) {
if(score >= 95){
System.out.println("A++등급입니다.");
}else {
System.out.println("A등급입니다.");
}
} else if(score >= 80) {
if(score >= 85){
System.out.println("B++등급입니다.");
}else {
System.out.println("B등급입니다.");
}
} else if(score >= 70) {
if(score >= 75){
System.out.println("C++등급입니다.");
}else {
System.out.println("C등급입니다.");
}
}else {
System.out.println("D등급입니다.");
}
}
}
|
cs |

블럭 {}
- 여러 문장을 하나로 묶어주는 것
- 만약 if 조건문에서 실행할 문장이 하나라면, if(조건문) 명령문; 이렇게 {}가 생략될 수 있음
조건식의 다양한 예

SWITCH
switch(조건식) {
case 값1 : 조건식의 결과가 값1과 같을 경우 수행할 문장;
break;
case 값2 : 조건식의 결과가 값2와 같을 경우 수행할 문장;
break;
default : 조건식의 결과와 일치하는 case문이 없을 때 수행할 문장;
}
- 처리해야 하는 경우의 수가 많을 때 유용한 조건문이다.
- break;를 작성해 주지 않으면 switch문 끝까지 실행된다.
- default 문 생략 가능
실행 흐름
1. 조건식을 계산한다.
2. 조건식의 결과와 일치하는 case 문으로 이동한다.
3. 해당 case문의 문장들을 수행한다.
4. break; 를 만나거나 switch 문이 끝나면 switch 문 전체를 빠져나간다.
switch 문의 제약 조건
1. switch 문의 조건식 결과는 정수 또는 문자열 이어야함.
2. case 문의 값은 정수 상수(문자포함), 문자열만 가능하며, 중복되지 않아야 한다.
int num, result;
fianl int ONE = 1;
switch (result) {
case '1' : // OK. 문자리터럴 (정수 49와 동일)
case ONE : // OK.정수 상수
case "YES" : // OK 문자열 리터럴
case num : // Error 변수 불가능
case 1.0 : // Error 실수도 불가능
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
class Control2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int month = 8;
String monthString = "";
switch (month) {
case 1: monthString = "January";
break;
case 2: monthString = "February";
break;
case 3: monthString = "March";
break;
case 4: monthString = "April";
break;
case 5: monthString = "May";
break;
case 6: monthString = "June";
break;
case 7: monthString = "July";
break;
case 8: monthString = "August";
break;
case 9: monthString = "September";
break;
case 10: monthString = "October";
break;
case 11: monthString = "November";
break;
case 12: monthString = "December";
break;
case 0: case 13:
System.out.println("이런식으로 case 문을 사용할 수 있습니다.");
break;
case 15:
default: monthString = "Invalid month";
}
System.out.println(monthString);
}
}
|
cs |

FOR
for(초기화; 조건식; 증감식) {
조건식의 결과가 참인 경우 반복적으로 실행하고자 하는 문장;
}
- 실행 순서
1. 초기화
2. 조건식
3. 조건식이 참일 경우 문장 수행
4. 증감식
5. 조건식이 거짓이 될 때 까지 반복
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class Control3_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("for 문이 " + (i + 1) + "번째 반복 실행중입니다.");
}
System.out.println("for 문이 종료된 후 변수 i의 값은 " + i + "입니다.");
}
}
|
cs |

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
class Control3_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1번
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i = i * 2) {
System.out.println("1번 i는 현재 " + (i) + "입니다.");
}
System.out.println();
// 2번
for (int i = 10; i >= 1; i--) {
System.out.println("2번 i는 현재 " + (i) + "입니다.");
}
}
}
|
cs |

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Control3_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 초기화 시 변수 2개 사용 가능합니다. 단, 타입이 같아야 한다.
for (int i = 1, j = 10; i <= 10; i++, j--) {
System.out.println("i는 현재 " + (i) + "입니다.");
System.out.println("j는 현재 " + (j) + "입니다.");
}
System.out.println();
// 이렇게 변수 2개를 사용하여 조건식을 구성할 수 있습니다.
for (int k = 1, t = 10; k <= 10 && t > 2; k++, t--) {
System.out.println("k는 현재 " + (k) + "입니다.");
System.out.println("t는 현재 " + (t) + "입니다.");
}
}
}
|
cs |

중첩 for
for(초기화; 조건식1; 증감식) {
조건식1의 결과가 참인 동안 반복적으로 실행하고자 하는 문장;
for(초기화; 조건식2; 증감식) {
조건식2의 결과가 참인 동안 반복적으로 실행하고자 하는 문장;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Control3_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 2; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "단 시작합니다.");
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println("j는 현재 " + (j) + "입니다.");
System.out.println(i + "*" + j + "=" + (i * j));
}
}
}
}
|
cs |

향상된 for
for(타입 변수 이름: 배열 or 컬렉션) {
배열 or 컬렉션의 길이만큼 반복적으로 실행하고자 하는 문장;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class Control3_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int e : arr) {
System.out.print(e + " ");
}
}
}
|
cs |

임의의 정수 만들기
Math.random() => 0.0과 1.0 사이의 임의의 double 값을 반환 ( 0.0 <= Math.random() < 1.0 )
1부터 5 사이의 random 한 정수 값 구하기
1. 0.0 * 5 <= Math.random() *5 < 1.0*5
2. (int)0.0 <= (int)(Math.random()*5) < (int)5.0
3. 0 + 1 <= (int)(Math.random()*5)+1 < 5+1
4. 1<= (int)(Math.random()*5)+1 <6
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
class Control4_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 괄호 { } 안의 내용을 20번 반복
// 1. 1 ~ 10 사이의 난수를 20개 출력하시오.
// 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
// 2. -5 ~ 5 사이의 난수를 20개 출력하시오.
// -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
// 1번
// System.out.println(Math.random() * 10); // 1. 0.0 * 10 <= x * 10 < 1.0 * 10
// System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 10)); // 2. 0 <= (int)(x * 10) < 10
// System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 10) + 1); // 3. 1 <= (int)(x * 10) + 1 < 11
// 2번
// System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 11)); // 0 ~ 10
System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 11) - 5); // -5 ~ 5
}
}
}
|
cs |

WHILE
while(조건식) {
조건식의 결과가 참인 동안 반복적으로 실행하고자 하는 문장;
}
실행 순서
1. 조건식
2. 조건식이 참일 경우 문장 수행
3. 조건식이 거짓이 될 때 까지 반복
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Control5_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 10; // while 반복 횟수 , 즉 for 문의 초기화
// while (i-- != 0) {
// System.out.println(i);
// }
// 위 코드와 같은 동작을 수행합니다.
while (i != 0) {
i--;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
|
cs |

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Control5_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 0;
while (sum <= 100) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
sum += ++i;
}
}
}
|
cs |

do - while
do {
조건식의 결과가 참인 동안 반복적으로 실행하고자 하는 문장
} while(조건식);
실행 순서
1. 처음 한번은 무조건 실행
2. 조건식
3. 조건식이 참일 경우 문장 수행
4. 조건식이 거짓이 될 때 까지 반복
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Control5_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int j = 1;
do {
System.out.println("do / while 문이 " + j + "번째 반복 실행중입니다.");
j++; // 이 부분을 삭제하면 무한 루프에 빠지게 됨.
} while (j < 20);
System.out.println("do / while 문이 종료된 후 변수 j의 값은 " + j + "입니다.");
}
}
|
cs |

break와 continue
break : 자신이 포함된 하나의 반복문을 벗어남
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class Control6_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 0;
while (true) {
if(sum > 100)
break;
++i;
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("i = " + i);
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
}
|
cs |

continue : 자신이 포함된 반복문의 끝으로 이동
- 이동하고, 다음 반복으로 넘어감
- 전체 반복중에서 특정 조건시 반복을 건너뛸 때 유용함
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class Control6_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
// 3의 배수는 건너뜀 : 3, 6, 9
if (i % 3 == 0)
continue;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
}
|
cs |
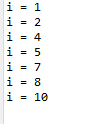
이름붙은 반복문
반복문에 이름을 붙여, 하나 이상의 반복문을 벗어남.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
class Control6_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
allLoop :
for (int i = 2; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j++) {
if (i == 5) {
break allLoop;
}
System.out.println(i + " * " + j + " = " + (i * j));
}
}
}
}
|
cs |
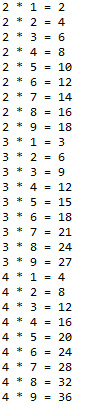
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Control6_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 2;
allLoop :
while (true) {
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j++) {
if (i == 5) {
break allLoop;
}
System.out.println(i + " * " + j + " = " + (i * j));
}
i++;
}
}
}
|
cs |
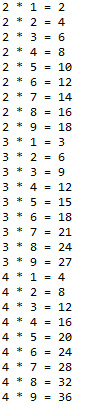
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Control6_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
allLoop : for (int i = 2; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j++) {
if (i == 5) {
continue allLoop;
}
System.out.println(i + " * " + j + " = " + (i * j));
}
}
}
}
|
cs |